Rand:�� �Howdy, SEOmoz fans. Welcome to another edition of Whiteboard Friday. This week we have a very special guest with us, Stefan Weitz, director of Bing.Stefan:�� �How are you doing?
Rand:�� �Stefan, thank you so much for joining us.
Stefan:�� �Sure.
Rand:�� �Really appreciate it.
Stefan:�� �It's on the way home. It's actually better for me this way.
Rand:�� �So, Stefan has two great distinctions. Number one, you were recently honored best hair at Bing. Is that right?
Stefan:�� �That was actually true and it was by mistake. One day I woke up and I had long hair and then I was afraid of getting scissors near my head and so I won't cut it now.
Rand:�� �That's phenomenal. And second, you are tasked with dealing with messy cleanup from incorrect PR that happens on the Internet and in major media sources.
Stefan:�� �Sometimes PR that I actually create. It's like job security over and over again.
Rand:�� �That's great. Well, let's see if we can't create some job security for you here today on Whiteboard Friday.
Stefan:�� �I'm sure we can.
Rand:�� �So we are going to get into some of the clickstream topics, but the first thing I actually wanted to chat about is something that you and I were talking about before this session. I think it will be of big interest to a lot of webmasters. So Bing obviously is gaining some nice market share, having a significant impact. Clearly Google is thinking you guys are more and more of a threat, which has got to feel a little flattering. It's got to be a nice feeling.
Stefan:�� �Well, I mean certainly it's good to know that. I mean, no one's really gained share against Google since Google launched. And look, they do a phenomenal job and they have for years and they've served us well for over a decade. So, yeah, it's nice to see us actually, between us and our Yahoo-powered search or the search that we power for Yahoo as well, I mean, you're talking between 26 and 30 percent of queries are now served by a Bing engine, which is great. The engineers love to see their work being used. There's nothing worse as engineers, as we all know, than writing something that never gets used.
Rand:�� �Oh boy. I can tell you some frustrations we've had on that front. Now, in terms of Bing and Google, one of the things that is really interesting is this New York Times story that came out this past weekend around JCPenney. So a search consultant was using Open Site Explorer, digging through the backlinks . . .
Stefan:�� �Nice plug.
Rand:�� �Yeah, it was a nice plug. Oh yeah, I have to plug SEOmoz on Whiteboard Friday. That's very important.
Stefan:�� �Okay. Make sure we're clear on that.
Rand:�� �So they're digging through these backlinks and they're finding a lot of what look like manipulative and paid links that apparently an agency that JCPenney had hired to do some search marketing work for them had purchased to help inflate their ranks. And for a year plus, or nine months plus, they'd been ranking number one, number two, number three at Google and fairly well, reasonably well on Bing, for most of this time for a lot of big searches. So one of the big ones we talked about was "dresses" and "bedding" and these kinds of generic terms. So the New York Times writes this article. That afternoon, Google sort of responds and says, "Hey, we're taking some punitive action against them." In the article they talked about this.
Stefan:�� �A penalty basically, yeah.
Rand:�� �Now, we did a search right before this Whiteboard started, and we searched for "JCPenney dresses."
Stefan:�� �That's right.
Rand:�� �And JCPenney is not in the top three results.
Stefan:�� �That's where it got weird for me, actually. I mean, look, I get . . . there are certainly, it's well within Google's rights to say, hey, we want to manually penalize a domain for any number of reasons. That happens. We generally don't like to use a lot of manual re-ranking. We like to try it algorithmically if we can because that just seems like it's actually a more scalable fashion. But you're right. What's happening here, I think, is they've kind of gone a little too far down the path of penalization. Because literally as we looked at, "JCPenney dresses," probably the best P1 result would be JCPenney's dress site, I would think. Right?
Rand:�� �Right.
Stefan:�� �And now it doesn't appear anywhere on that P1, page 1.
Rand:�� �And in fact, I think the fourth result is like their mobile page, which is sort of a weird result to have in the web search.
Stefan:�� �Yeah.
Rand:�� �And this is happening because of this penalization system. One of the things that is really curious, I think, for a lot of webmasters, how are Bing and Google ever going to beat this problem on a macro scale?
Stefan:�� �That's an excellent question. So, there's a couple ways. There is the kind of short-term thing we're looking at from the ranker itself. Like, are there particular classes of link farms that we know are of low quality? Can we kind of apply some kind of discount to links that are coming in from what appear to be low-quality link farms? There's stuff we can do there, which we'll do too. We'll all look at these methods to figure out . . .
Rand:�� �There's a lot of machine learning that goes into that process, to say like here's a big set of what we think are spam links.
Stefan:�� �Yes.
Rand:�� �So as a webmaster, you better not look like spam, either the spam that exists today or the spam that's going to exist tomorrow because a classifier is going to catch that.
Stefan:�� �That's right. And this is a machine, right? And so you could get ostensibly swept up into one of these categories, right? We actually had someone mail us, a couple weeks ago, who had a site that actually looked like it may have been a spam site. It actually wasn't, but it had a lot of characteristics of what we consider them to be and so she was getting a penalty it looked like on her site. And so we said, "Okay, we can't tell you exactly what to fix, obviously, but here's some things you ought to look at." So there are some things that are happening there.
But, I think, if we go a little bit further, there are two things. We, Google, everyone, Yahoo, Bing, we all use human judges to kind of measure relevancy.
Rand:�� �Right. Google has this big worldwide distributed team of search quality raters, and you guys have a team as well.
Stefan:�� �Same thing. HRS, yeah, same thing, and so human raters actually look at this. The challenge we have, we were looking over the weekend, all the engineers, we were all in threads over the weekend looking at this problem and we said, gosh, you know the problem is for bedding, the JCPenney result wasn't bad to a human. Maybe it shouldn't have been P1, but P4? I don't know. Actually if you ask a human to say, "Is this a good result?" They go, "Yeah, it's actually pretty good."
Rand:�� �So this is why you're not going to get spam quality raters who are saying, oh, JCPenney ranks first for bedding, complain and spam report.
Stefan:�� �Exactly.
Rand:�� �No. JCPenney seems perfectly reasonable.
Stefan:�� �That's right. And so if we took it all the way out, we actually realize that you likely would decrease any CG or the kind of cumulative gain that we get as we measure relevance. So if you yank it out, you actually then, people go, "Wait, where did JCPenney go? They sell bedding." And so it's one of those weird things actually to try to correct for when you have a situation like this.
But in the longer term, this really points to the bigger challenge with search, which is stopping thinking of search as just a way to navigate the collection of links across the Web. Essentially, we've been doing the same kind of search now for over a decade, right? It's basically anchor text and page rank and inbound links, and that's how we've kind of decided what page is best for a particular term.
Rand:�� �And you think that this model of anchor text, page rank, or in Bing's case static rank and diversity of incoming domains, that's going to fade out to something else? Or it's going to be bolstered by other things?
Stefan:�� �Yeah. I think that'll be around for a long time. So don't worry. You don't have to like go and sell off. Don't call up Rand and say, "I want out." That's all fine. I don't know. I always think of you as . . .
Rand:�� �That I sell links? Really?
Stefan:�� �No. You know orange is Bing's color. That's why I took the color.
But there are signals beyond this. That'll be for a long time. But what we're looking at, and the example I was using today with some engineers was, you do a query ? not to pimp Bing here ? but if you do a query for, say, shoes on Bing, we actually . . . the first answer now, we actually fire off what's called a visual search gallery, which basically is a way to navigate 3,000 pairs of shoes using a more familiar visual metaphor. So you can say, "Okay, I actually want high heels. I want patent leather. I want black."
It's kind of like applying metadata to your query, and it actually rejiggers the results in real time based on what it is you're trying to do. Because in many cases, people do come to engines and they put in one word, they put in two words, very ambiguous. "Shoes" is a horrible query, right? But we get a lot of that. So the question really is do we just take "shoes" and just try to throw back everything we can against that word, which of course is going to be fraught with problems.
Rand:�� �Right. Shoes.com. Online shoes. Shoe store.
Stefan:�� �Yeah, exactly. Is that the right thing? Really, is something that ambiguous actually calling out for a more reasonable approach where we say, "What do you mean?" Kind of like if you and I were talking and I would say, "Shoes." And you go, "What? What, like dress shoes? What are you asking? Do you want to buy shoes?" So we have conversations. And today, engines, they kind of fail. They're very autonomic. They're kind of an in and out type transaction. And we think, with things like Visual Search, we're able to actually start to say, "Okay, great. What do you really mean with that query," and try to pivot and help people refine.
Rand:�� �So Google's got kind of on the left side those related searches or search suggestions. You guys have search suggestions.
Stefan:�� �I think the left and the top. On the top. We actually do an answer bar at the top. Those are interesting ways of conversation modes, but we're even looking at ways to go a little further than that without getting into Clippy, which I love Clippy, but not everyone loves Clippy. So something like that without being annoying.
Rand:�� �I always worry that people are going to think Roger, our mozBot, is Clippy-like.
Stefan:�� �Oh, you know what? Can we borrow him for our . . .
Rand:�� �You totally can. We have a current asking price. I'll let you know after this Whiteboard Friday.
Stefan:�� �So there's that. Longer term, we're looking at how we think of the Web really as a representation of the physical world itself. So we understand that, the weird example I was giving you earlier, "Inception" is a movie. You and I understand that "Inception" is a movie. We understand "Inception" as a movie has a certain number of characteristics. Movies have reviews. They have show times. They have previews. They have trailers. They have pictures. They have conversations on Twitter.
Rand:�� �So are you saying, from a marketer's standpoint, let me imagine that this is the knowledge that I've got about "Inception." It's a movie. Do I then want to say, "Oh, I should make sure that a page about 'Inception' of mine has things like information about who is acting in it and maybe a video of the preview or the trailer and reviews and data like that and that it's in the movie realm rather than just being the page on the Internet with the most inbound links that say 'Inception.'"
Stefan:�� �Yeah, because honestly, what's going to happen is . . . we just did this, actually, with our last release. We have become much smarter about these objects on the Web. So we do actually know "Inception," and that's a weird example. Think of like, "Casablanca," which actually has multiple editions that have been re-released over the years and there are different release dates.
Rand:�� �And there's an actual city.
Stefan:�� �Exactly, right that too. But now we can begin to say, okay, this "Casablanca" on Netflix is the same "Casablanca" you can buy on Amazon or you can rent on iTunes. That's actually a lot harder than you think because the movie domain is not as clear.
Rand:�� �So this is like an entity association type of algorithm.
Stefan:�� �Yeah, exactly. And so that's what we're going to see more and more search heading towards, we believe, is that us understanding the Web again literally as a representation of the world and not just a bunch of links and pages and static text. That offers up an entirely new way to think about ranking.
Rand:�� �I guess that would be my last question on this before we move on to the clickstream stuff is, as a marketer, what should I be thinking about to be a step ahead as this is coming forward? It sounds like there's naturally going to be some brands who are doing these types of things already. I'm a small website. I'm starting out. I review movies. I want to make sure that Bing and Google know that my stuff is good. What should I be thinking about?
Stefan:�� �Today, all the classification is done in a very machine learned process. Ideally, there are defined microformats you have for a lot of these things. I can see a lot of that coming down the road. Even like Facebook's Open Graph system has a limited amount of RDF.
Rand:�� �Right. I can say, "This is me. Rel=me."
Stefan:�� �Or you can say something like, I forget the actual phrasing, but basically you can say, "This page is about a movie," for example. I would be watching very carefully what standards or even what proposed standards begin to evolve to help describe things that you're working on in a more concrete manner. So if you are selling, let's say your business is selling sheet music of 1930s swing songs, as an example. There will be a time in the not too distant future, in most people's opinion actually, not just mine anymore, where you're able to actually mark up this piece of sheet music that I'm selling. There will be kind of an ontology or some kind of taxonomy which lets the marketers say, this is from, I can't think of composers from the 30s, but some composer ? composer=foo, decade=foo, year=foo ? and actually begin to describe this thing, this object as an object and not as simply a web page, hoping that we crawl and parse it correctly. Because, frankly, crawling and parsing is a very messy, expensive, and inaccurate science.
That's the brave new world. But again, for now, just keep doing great SEO work, but don't buy links.
Rand:�� �Don't buy links. Let's move into another really interesting story around this clickstream stuff. So a couple weeks ago . . . no, I'm sorry. I guess it was about a month and a half ago. So Google built a little honeypot, right? Essentially they say, we think that . . . well, because Google and Bing are both using these signals of clickstream data, Google says we think we can engineer this clever system to catch Bing by using a nonsense word.
Stefan:�� �Yes.
Rand:�� �And essentially what they caught you guys doing is not building a system that was robust enough to recognize, oh, when we have very few signals about some random nonsense word, maybe we should be tossing those out because otherwise we could be manipulated in a way that would make us look bad.
Stefan:�� �Right. Yeah, let's do it.
Rand:�� �So let's go with an analogy here. This is a terrible representation of the island of Manhattan, right?
Stefan:�� �Wow.
Rand:�� �So here's maybe here's Central Park. Does that sound . . .
Stefan:�� �That's better. Now I . . .
Rand:�� �Now you're there. Washington Heights right here.
Stefan:�� �My mom grew up in Harlem right over there.
Rand:�� �My sister lived right here for a while. This is kind of fun.
Stefan:�� �Yeah.
Rand:�� �So, navigating the island of Manhattan are tens of thousands, hundreds of thousands of vehicles.
Stefan:�� �Yes.
Rand:�� �Maybe even a million vehicles. I'm not exactly sure. There's like 11 million people in the city. So if I get a Bing navigation system, Bing is going to tell me based on traffic patterns and the weather and the time of day which way I should go in New York City. Hang with me, this analogy works.
Stefan:�� �It does work, I think.
Rand:�� �So Bing has this nice satellite that's orbiting up here.
Stefan:�� �This is hypothetical, by the way. There is no Bing satellite watching traffic.
Rand:�� �Right. This is a pure analogy.
Stefan:�� �Everyone is going to be freaking out.
Rand:�� �So there's a satellite that's sort of watching and saying, "Oh here, look at traffic patterns." And Google's got their nice satellite.
Stefan:�� �Yeah. They actually do have one though, watching everything you do.
Rand:�� �That's good to know.
Stefan:�� �I'm sorry. Was that out loud?
Rand:�� �Oh boy, you're going to get into big trouble.
Stefan:�� �There goes that sponsorship.
Rand:�� �So they're both watching all the traffic patterns and what they see is, oh, you know what? The best traffic pattern at 4:00 p.m. on a Tuesday for a midsize car is to go down the West Side. The East Side is just a mess. Park Avenue, nobody wants to be there, but the West Side, that looks quite good. So they're directing cars this way.
Now, what Google did in this instance, taking this analogy to search is essentially say, "Oh, you know what? It's 2:00 a.m. on Christmas Eve. There's virtually nobody on the road and we're actually going to grab . . . you know what? We're going to make this weird, new three-wheeled blue vehicle that no one has ever seen before and we're going to send them this weird circuitous route. In fact, they're going to have to cross over Central Park and around there." Oh my gosh, just to get down to Wall Street.
And so Bing is monitoring this and they see, all right, well there's one blue car traveling on Christmas Eve at 2:00 a.m. This is the route it takes. And then next Christmas Eve, when a blue car shows up, some Google engineer goes home and gets into his blue car and checks, "Oh look, that's the route that Bing is sending me. They must be . . ." What do they call it?
Stefan:�� �Copying.
Rand:�� �Right, cheating off my test.
Stefan:�� �Yes, copying, cheating.
Rand:�� �It doesn't seem like an entirely accurate analogy, but it's pretty good. Well, the cheating off the test results seems . . . it seems like the kind of way that things are going. So Google and Bing are both looking at where people are going on the Web, what they're clicking on, when they search for something, what do they get to next, what do they seem to be happy with, did they refine those search queries and do other types of searches, can we learn based on that behavior? Seems like a very smart way to go. And you saw, there was an ex-Google engineer who went on Quora and said, "Oh yeah, when I worked at Google, we did exactly the same thing."
Stefan:�� �Oh, yeah. That's kind of what I was so perplexed about is that it's not . . . (a) we've said we've been doing this for years. We've actually, since '07, been doing clickstream analysis. It's an opt-in thing. Again, it's anonymous. People opt-in to it.
Rand:�� �And the Google engineers who checked this, they went home and they installed Internet Explorer with the toolbar and opted in.
Stefan:�� �And opted in, correct.
Rand:�� �So that they would show you guys this data.
Stefan:�� �Exactly. And so what? We made no secret of this at all. This is actually, we think, a very valuable signal to have. Now, that being said, I can tell you, without getting into all the details, it's not a huge signal. It's one of thousands of signals we use to actually calculate PR.
Rand:�� �I bought thousands of Mechanical Turkers and had them all click your results for SEO, and I didn't move one position. So I'm really upset about that.
Stefan:�� �Aw, dammit.
Rand:�� �Because based on what I saw here I thought . . .
Stefan:�� �You thought you could nail them, right?
Rand:�� �I thought I could just get it.
Stefan:�� �So that's the first thing is that we, and Google even themselves uses this data. They are kind of going back and forth if they do or not. But look, we know for deep links, likely they use toolbar plus . . .
Rand:�� �Right, sure. Yeah. If I click that JCPenney search result, there's these other links that pop up there, and they're usually the same ones that people search for most often and click on most often.
Stefan:�� �Exactly.
Rand:�� �That's a good customer experience. You actually want to encourage that.
Stefan:�� �Oh, totally.
Rand:�� �They have, I think, they've got a site speed ranking factor as well. How fast is the site? And they'll show you that data in Webmaster Tools and that comes from the toolbar.
Stefan:�� �That's right.
Rand:�� �I think they say it comes from the toolbar inside Webmaster.
Stefan:�� �Oh, well, there you go. I'm not throwing mud at all. I think it's actually a very valuable thing. What was frustrating to me, I think, is just the fact that it was . . . they successfully proved something we've said we've done now for three years, which is great. They've given me a proof.
Rand:�� �Well, to be fair, you guys probably should have written something that said, hey, if someone builds a honeypot and uses these small signals . . . so they've got a little gotcha.
Stefan:�� �Absolutely.
Rand:�� �But I think maybe it was the press who blew it into a pretty big gotcha.
Stefan:�� �Yeah. At the end, it's really, you're right. And we actually were talking to Harry, who kind of runs all engineering for Bing and he's like, "If anything, they helped us kind of find a bug. Maybe we should be throwing out if we only have one signal." Because really, the reason that 7 of the 100 that actually tried the beta with . . . so we actually didn't fire. They gave 100 terms and 93 we didn't actually do anything.
Rand:�� �So they had 100 blue cars.
Stefan:�� �That's right.
Rand:�� �You only tracked a few of them.
Stefan:�� �We tracked all of them because they have clickstream, of course, but we just didn't use the clickstream in our ranker. I would have to look at the probe. Something triggered something somewhere and said, "Even though we have this signal from toolbar, something doesn't feel right. We're not going to fire anything at all." So seven of the hundred actually did, and that was, probably where we had . . . maybe the engineers got a little happy at home and they had a couple gin and tonics and started clicking like crazy on the link and that gave us more data than the other terms. Who knows. But the point is that we think it's a valuable thing to use. We think the behaviors of customers on the Web who have said they want to help improve the product through their usage, we think it's the customer's behavior that they're giving to us to use and refine.
Rand:�� �Well, this would be like in the SEOmoz web app, for example, us saying, "Oh, you know what? When people go from their on page to their ranking report, lots of people are doing that, let's put those tabs right next to each other."
Stefan:�� �Exactly.
Rand:�� �Let's do it. It seem pretty natural.
Stefan:�� �One of the arguments that I had heard from people on the Web was, "You just shouldn't be using it. It's just not your data." And I think that the Web was built on this notion of collective intelligence. And frankly, Google has a lot of search data. We know this, right? So to ignore it just because it comes from a competitor, it seems . . .
Rand:�� �Well, you're not just doing this on Google, right? You do it on Yahoo.
Stefan:�� �Oh, yeah. The clickstream, right.
Rand:�� �If somebody searches SEOmoz's website, you'll see that if I use Internet Explorer.
Stefan:�� �Yes.
Rand:�� �So it doesn't matter the specific source. Right?
Stefan:�� �That was the big brouhaha.
Rand:�� �So let me ask, from a marketer's perspective. I think a lot of people in search observed this behavior and then said to themselves, "Wait a minute. I can drive blue cars. Can I influence things through the clickstream?" Is that something where you've already seen an uptick in manipulation?
Stefan:�� �There have been attempts, I'm sure. But the reason this was so successful, if you call 7 out 100 successful, was because they were nonsense words, words that no one would ever use.
Rand:�� �Literally zero search volume ever.
Stefan:�� �Precisely. They were made up words. And then Google did a manual re-rank of those in their index. So when you searched for them on Google, this one site would pop up. It was a completely . . . and even that, even with that explicit signal, only 7 out of 100 actually worked. So I would tell you that it probably isn't a good use of your time to be doing a lot of clicking on clickstreams to try to rank higher.
Rand:�� �Gotcha. All right. Well, good to know. We'll try something else.
Stefan:�� �Exactly. But what it does say is that if you rank organically high generally . . . do what you generally do to rank high organically, because that is a factor. In other words, if you do rank at P2 on Google or P2 on Bing and people are clicking through, they search for SEOmoz and click on that link. It's just good practice.
Rand:�� �So you're saying one of the things that SEOs maybe need to be thinking a little bit more about is not just getting that position, but making sure that once you have that position, people want to click on it.
Stefan:�� �Are you maximizing? That's right. Your caption, your title, all this stuff.
Rand:�� �Right, that title and that meta description.
Stefan:�� �Exactly. Make sure . . . you want that click after they search for you if it is the right site for that particular term. So yeah, that was "Copygate" a couple weeks ago.
Rand:�� �Well, I'm glad we're done with that.
Stefan:�� �It was fun.
Rand:�� �Yeah, I'm sure you want to do that all the time.
Stefan:�� �One hair is grey now because of that.
Rand:�� �I have more than that. So, third question, and last question, but I think a lot of people are interested. What's some new stuff that's coming out at Bing? Either for searchers or for webmasters, because I know Webmaster Tools has sort of been in a little bit of a stagnant state for a little while.
Stefan:�� �It's catch-up, I'd say. We just actually brought in Duane Forrester who you guys might know out in the community.
Rand:�� �Yes, absolutely.
Stefan:�� �Duane now works on the Bing team, and he is in charge of a lot of stuff. He'll be out there in the forums with you guys a lot more and across the entire ecosystem for Bing. Duane will be our guy out there in the space. We updated the Webmaster Tools, I think it was a couple months ago now. It's all Silverlight-based. There's still some areas I know we need to catch up in.
Rand:�� �I won't give you too hard a time, but the Silverlight . . .
Stefan:�� �I know.
Rand:�� �When you install Silverlight functionality, there are a few things you lose that you have on the HTML side.
Stefan:�� �Yeah, that's frustrating. But the good news is that we've staffed a team of actually more than we had before. So those guys are cranking on the new functionalities. We know that we have to do a better job there. We know it. No one's hiding like, "No, we're hot. Let's just keep going." We think we do a good job. We can do a lot better.
And then as far as new stuff for consumers is concerned, I think one of the most interesting things that we'll have rolled out this week ? since this is Friday, I can talk about it now ? is this new thing called tiles. You'll see them on the page. Think of it now as really a user experience enhancement. In essence, what we found was that people are able, when they see basically a page, if you look at the page and you do a query for something like, I don't know, let's just do one. What's that new Natalie Portman film?
Rand:�� �Oh, that looks terrible. Not "Black Swan."
Stefan:�� �Not "Black Swan," the other one.
Rand:�� �Oh, with Ashton Kutcher.
Stefan:�� �So we'll let's call it "new Natalie Portman film." I don't what it's called, but whatever it's called.
Rand:�� �That's probably a good search. Since we can't remember, lots of people are querying that.
Stefan:�� �That's probably true. I can see the billboard in my head, but I can't . . .6
Rand:�� �I can see the preview. Clearly bad branding.
Stefan:�� �God, no kidding. What the hell? Anyway, so you do a search for this on Bing and you get all the results here, all of the organic results. And what you're seeing now with the introduction of tiles is a little visual indicator here on the side for a couple of these results that come from what we call authoritative sites. So you might have one from IMDB here, one from Rotten Tomatoes, one from, I don't know, Flixster, etc. We're actually going to be pulling in metadata from those sites. So you have the average 77% fresh rating here. Flixster might have their rating, IMDB can have their rating. But what we're doing now is we 're actually . . . because we know people actually are able to figure out the results they're looking for if you append some kind of visual cue onto the page. So by adding on these visual cues for these kind of authoritative sites or high-quality sites. . .
Rand:�� �Are they sending data specifically to you, or are you guys pulling that from their page without them even having to do anything?
Stefan:�� �No. In this case, there's been some agreement with these guys.
Rand:�� �So it's like when Google was testing some of their rich snippets, what they call recipes and yeah, yeah, yeah.
Stefan:�� �So that I think . . . we'll see. It's just a test now, but we'll see how it works. Internal flighting have been pretty successful with it, and it really provides a way for people to actually find what they're looking for much faster, because you know the logo for IMDB, you know the logo for Flixster, maybe.
Rand:�� �And if I think I'm a trusted website, hopefully in a few months I'll be able to submit something to you, give you some data, and you could potentially give me this kind of result.
Stefan:�� �Yeah. Nothing to announce yet, but you're getting the idea. Exactly. This notion of how do you kind of ingest third party content more successfully and make it more discoverable to people. So that's kind of fun.
And then, of course, a lot of mobile stuff has come out in the past couple months. You'll see more of this going forward. But really focusing on the scenarios as you're on the go. You know, unfortunately, it's not out yet, so I can't talk about it. Just let me think for a second. It's so awesome. You're going to love it. Just wait.
Rand:�� �Is it on all Nokia devices now?
Stefan:�� �It should be. We'll do a follow up. Next time, I'll actually bring a machine and we can actually demo stuff.
Rand:�� �Oh, that sounds awesome. I love it. Well, Stefan, this has been phenomenal stuff. I think people really appreciate you and Duane particularly being out in the community talking to webmasters about this type of stuff. I hope you'll join us maybe in the comments if folks have a couple questions.
Stefan:�� �Absolutely. Just don't make fun of my hair. That's all I ask.
Rand:�� �It was windy outside before he got up here.
Stefan:�� �Sure.
Rand:�� �Thanks so much for joining us. Thanks, everyone. Take care. We'll see you again next week for another edition of Whiteboard Friday.
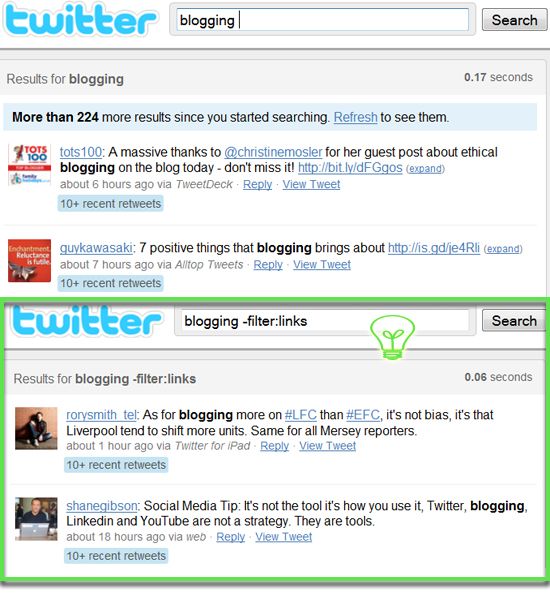

 Twitter tips | facebook tips will list either ?twitter tips? or ?facebook tips? (or both):
Twitter tips | facebook tips will list either ?twitter tips? or ?facebook tips? (or both):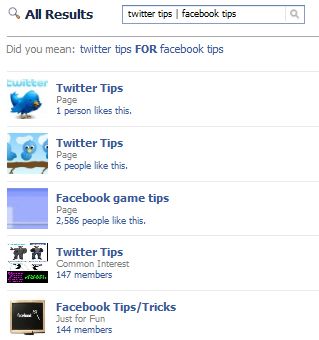 The same operator works for the auto-complete drop-down, which means you can see much more varied results there as well:
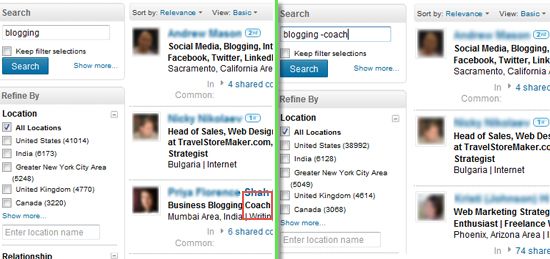
The same operator works for the auto-complete drop-down, which means you can see much more varied results there as well: This supported operator gives at least some freedom in controlling your search results? proximity and variety. Let?s hope Facebook will eventually come up with more.
This supported operator gives at least some freedom in controlling your search results? proximity and variety. Let?s hope Facebook will eventually come up with more.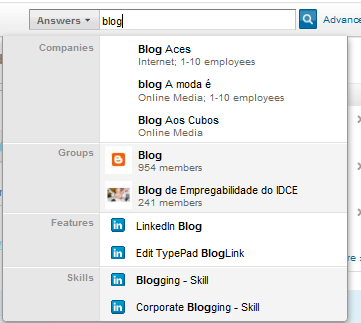
 Combine two search terms within one search if you, for example, want to find people who mention both ?blogging? and ?marketing? in their profiles:
Combine two search terms within one search if you, for example, want to find people who mention both ?blogging? and ?marketing? in their profiles: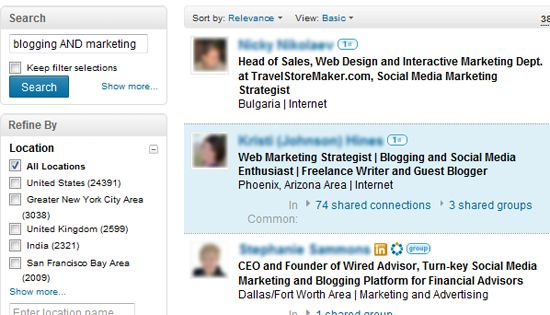 Choose to see at least one of your terms within search results. This one is similar to Facebook?s operator mentioned above. For instance, search for blogger OR freelance writer:
Choose to see at least one of your terms within search results. This one is similar to Facebook?s operator mentioned above. For instance, search for blogger OR freelance writer: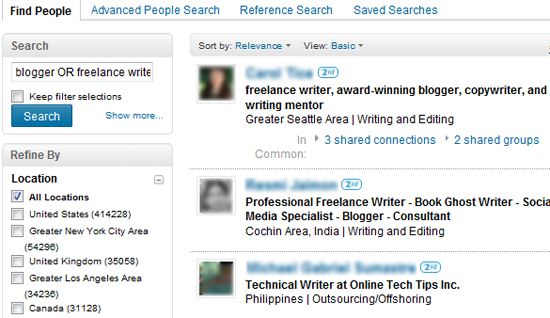





 What are Demand Media's secret ?agreements? with Google?
What are Demand Media's secret ?agreements? with Google? Google drops real estate search listings
Google drops real estate search listings "We have been using
"We have been using 







 Using a search engine like Google or Yahoo is the most common way customers look for products online. Without effective search engine optimization, your business may get left behind.
Using a search engine like Google or Yahoo is the most common way customers look for products online. Without effective search engine optimization, your business may get left behind. Our CEO,
Our CEO, 
Great Article Robbin! I wanted to add one more idea. Volunteer. We had a guy come in to apply for a job earlier this week and he really stood out from the rest of the applicants, because he was already doing SEO for free for a church. There are many organizations out there that don?t have the money to do SEO or Analytics, but would appreciate someone who could volunteer to do it for them. This is a great way to get a good letter of recommendation as well.
Thank you very much for this useful post. I appriciate for helping noobs.